MUMPS
Posted 04/08/2017
What is mumps?
- Mumps is a serious and highly infectious viral disease prevented by the measles-mumps-rubella (MMR) vaccination.
- Mumps is spread from an infected person by saliva or mucous droplets when coughing, sneezing, or talking.
- People with mumps are infectious and can spread mumps to others for 2 days before the swollen glands are noticed, until 5 days after.
- It can take up to 25 days for someone to develop the symptoms of mumps, after being exposed to someone who has mumps.
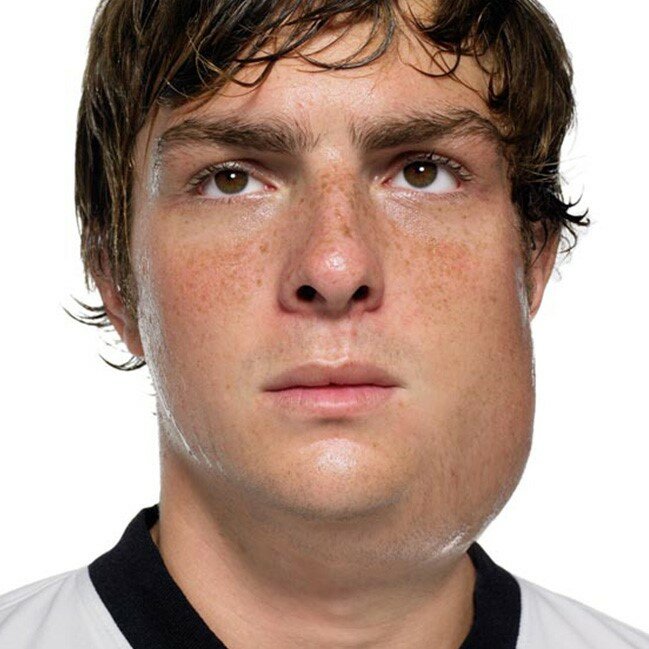
- Early symptoms of mumps include fever, headache, muscle aches, tiredness, and loss of appetite. The salivary glands on one or both sides of the face, cheeks or jaw may become swollen and sore after two days.
- Most people recover from mumps however some individuals can develop rare complications. Men and adolescent boys can experience pain and swelling in their testicles, which in rare cases can result in infertility. Females can experience ovarian inflammation. For pregnant women there is risk of miscarriage in the first three months. In some people mumps can cause permanent hearing loss. In very few cases, mumps can lead to inflammation of the brain and surrounding tissue (meningitis).
Protecting yourself and others from mumps:
- The best way to protect against mumps is to be vaccinated with two doses of the measles-mumps-rubella (MMR) vaccine.
- In New Zealand MMR vaccination is routinely given at age 15 months and again at four years. However, in Tonga and Fiji, mumps is not vaccinated against. The vaccine given is a measles-rubella (MR) vaccine.
- Contact your doctor if you are unsure if you have been vaccinated, or if you need to catch-up with a second dose. MMR vaccination is free for adults and children who have not received two doses of the MMR vaccine.
What should you do if you think you might have mumps?
- If you are at risk and are unwell – particularly with fevers and swollen glands on either side of your neck, you should see your Doctor straight away. If you can, phone ahead so that you are not sitting in the waiting room risking spreading mumps to others.
- Your Doctor will take tests to see if it is mumps, and will notify us at public health to support you and your family in preventing the spread of mumps to others.
- Apart from going to the Doctor, people who have mumps, need to stay at home away from others. That means they cannot attend day care, school, work, social activities, sports/recreation events. They should not use public transport or visit public places such as cinema’s or shopping malls.
- You can also phone Healthline for advice on 0800 611 116.
Key messages:
- Check you/your child has had x2 MMR vaccines. If not, see your Doctor or Nurse to get your vaccine(s)
- Know what the signs and symptoms of mumps are, and keep watching for them for 25 days after last exposure to someone with mumps, or for 25 days since the dance party
- If you think you have mumps, see your Doctor for testing
- If you have mumps, stay at home away from others for 5 days after the swelling in your glands started